Mobile Integrated Health Significantly Reduces Opioid-Related Deaths
JEMS
JUNE 11, 2025
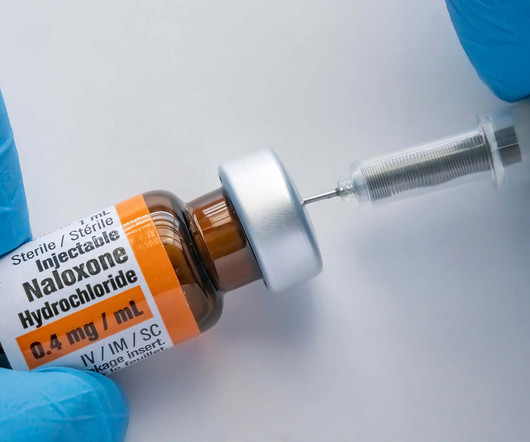
This includes ‘naloxone wake-up’ calls. Many times, when EMS providers administer naloxone to unconscious and apneic overdose patients, the patient becomes conscious, complaining of withdrawal symptoms induced by the use of naloxone. Also included within these kids is a local resource guide for help with SUD/OUD.






Let's personalize your content